Using Python scripts (beta)
Commands
BIMPYTHON
About BIMPYTHON
The new BIMPYTHON command enables you to query and manage data from a model within BricsCAD BIM, with a suitable .py Python script.
The Python scripts can be as simple as obtaining quantities and associated properties of objects and BIM entities, or as elaborate as implementing a series of calculations based on the model parameters available.
BricsCAD does not ship with a Python Shell, so the scripts would need to be prepared in a text or code editor application.
The Python Programming Language, together with its standard libraries, is embedded within BricsCAD BIM so there is no need for you to install them separately unless you have custom packages and libraries which you wish to use in your scripts.
Before using BIMPYTHON, you need to first turn on the virtual Python environment within BricsCAD.
Procedure: activating the Python environment in BricsCAD
- Open a new or a BricsCAD file where you would like to run a Python script.
- Type BIMACTIVATEPYTHON in the Command line and press Enter.
- You will be prompted: New current value for BIMACTIVATEPYTHON [1 for ON/0 for OFf] <1 for ON>:
- By default, the value should display <1 for ON>.
That means the Python environment is already activated.
However, If the value shows <0 for OFF>, type 1in the Command line and press Enter to confirm.
Or
- Open a new or a BricsCAD file where you would like to run a Python script.
- Access the Settings
 dialog
box.
dialog
box. - Tick the box where it says Activate Python under the
General subcategory within
BIM.
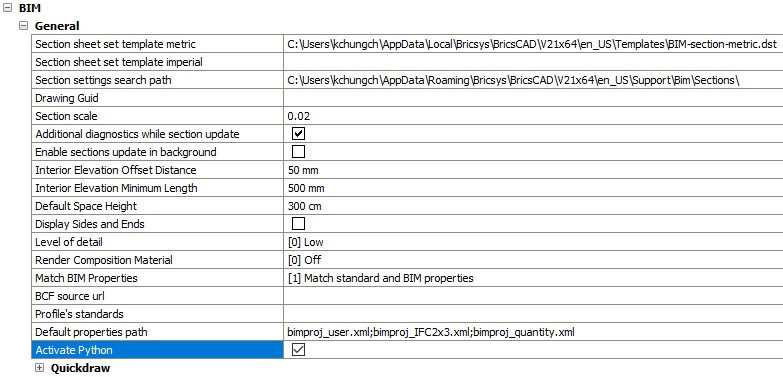
- Close the dialog box to confirm your updated settings.
Procedure: setting up a Python script with the BIMPYTHON module
- Before gaining access to the API, import or 'call' any desired modules you
wish to have in the script.
If they are not part of the Python Standard library, make sure they have been installed separately beforehand.
You can "import" a standard module, such as math and "import as" an external one, for example Pyplot, which is a collection of functions in the Matplotlib package:import math import matplotlib.pyplot as plt - With your desired libraries "called" in, the next step is to gain access to
the API in order to query the elements within the BricsCAD model. This is
the range of bim objects and serves as an entry point to the model.
Import the briqpy.bim_model:
from briqpy import bim_model - Now, you can query the model with these example
statements.
# Display info about the lengths of walls in the model lengths = [wall.prop('Length') for wall in bim_model.filter(Type='Wall')] print(f'wall lengths. max: {max(lengths)}, avg: {sum(lengths)/len(lengths)}')# Create a selection and print the objects bim_model.filter(Type='Wall', IsExternal=True).select() for wall in bim_model.filter(Type='Wall', IsExternal=True, Length=max(lengths)): print(wall)
# Get all parts of roof within 40cm range of all walls
roof_parts = bim_model.filter(Type='Roof').parts()
roof_parts_close_to_wall = bim_model.filter(Type='Wall').within_distance(40, 'cm', search_range=roof_parts) Whereas this is an example of a function statement to filter:
# Filter roof parts longer than 50 project units
def is_long(obj):
return obj.prop('Length') > 50
roof_parts.filter(is_long) # create a dictionary list
wall_info = [
{ 'Handle': wall.prop('Handle'),
'Length': wall.prop('Length'),
'Height': wall.prop('Height')
} for wall in bim_model.filter(Type='Wall')] # export to .json
import json
file = open('path/to/file.json', 'w+')
file.write(json.dumps(wall_info, indent=4))
file.close() # plotting a histogram
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(wall_info)
df.hist();
plt.show() # export to .csv
df.to_csv(r'path/to/file.csv', index = False, header=True) For more information on the BricsCAD API and its various classes, please visit the API chapter below.
Procedure: executing the Python script
- Open a new or a BricsCAD file where you would like to run a Python script.
- Type BIMPYTHON in the command-line and press Enter.
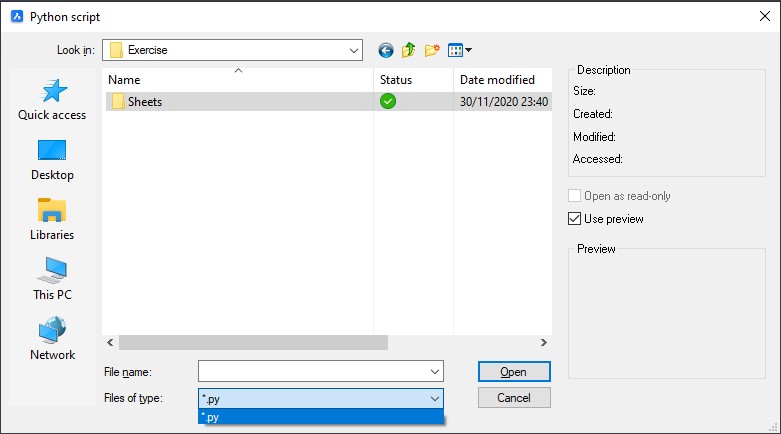
- A dialog box is displayed where you can only select a Python script file
(*.py). Select it and click Open to execute the
file.
- Unless you have specified the data to be exported or displayed in an external program outside BricsCAD, BricsCAD reports the output in the Command line panel.
API dictionary
Classes and syntaxes
prop(prop_name)- Returns the property value of the Object with the given name.
distance_to( other_obj, units='mm', distance_mode='exact' )- Calculate the distance between two Objects.
- Options for argument units: any units value form insunits ('Centimeters', 'Feet', 'Parsecs' etc.) and these abbreviations: 'mm', 'cm, 'm', 'km', 'ft'.
- Options for argument distance_mode: 'bbox_center', 'bbox', exact'.
parts()- Return the ObjectRange containing the sub-elements of this object.
parent()- The opposite of parts(), returns the parent object of this sub-element.
within_distance( distance, unit='mm', distance_mode='exact', search_range=bim_model )- Return the ObjectRange of objects that are within the distance of argument distance.
- Options for argument units: see distance_to.
- Options for argument distance_mode: see distance_to.
select()- Add Object to selection
deselect()- Remove Object from selection.
__eq__() and __hash__()- Makes Object interoperable with e.g. python set or dictionary.
filter( function )- Filtering this range with a function parameter.
filter( **conditions )- Filtering this range with conditions given as keyword arguments.
parts()- Return the ObjectRange of all the parts of all the elements in this range.
parents()- Return the ObjectRange of all parent objects of elements in this range.
within_distance( distance, unit='mm', distance_mode='exact', search_range=bim_model )- Returns the ObjectRange of objects that are within distance to any object in this range.
select()- Add Objects to selection.
deselect()- Remove Objects from selection.
__len__ ()- Return the number of Objects in this range.